Introduction
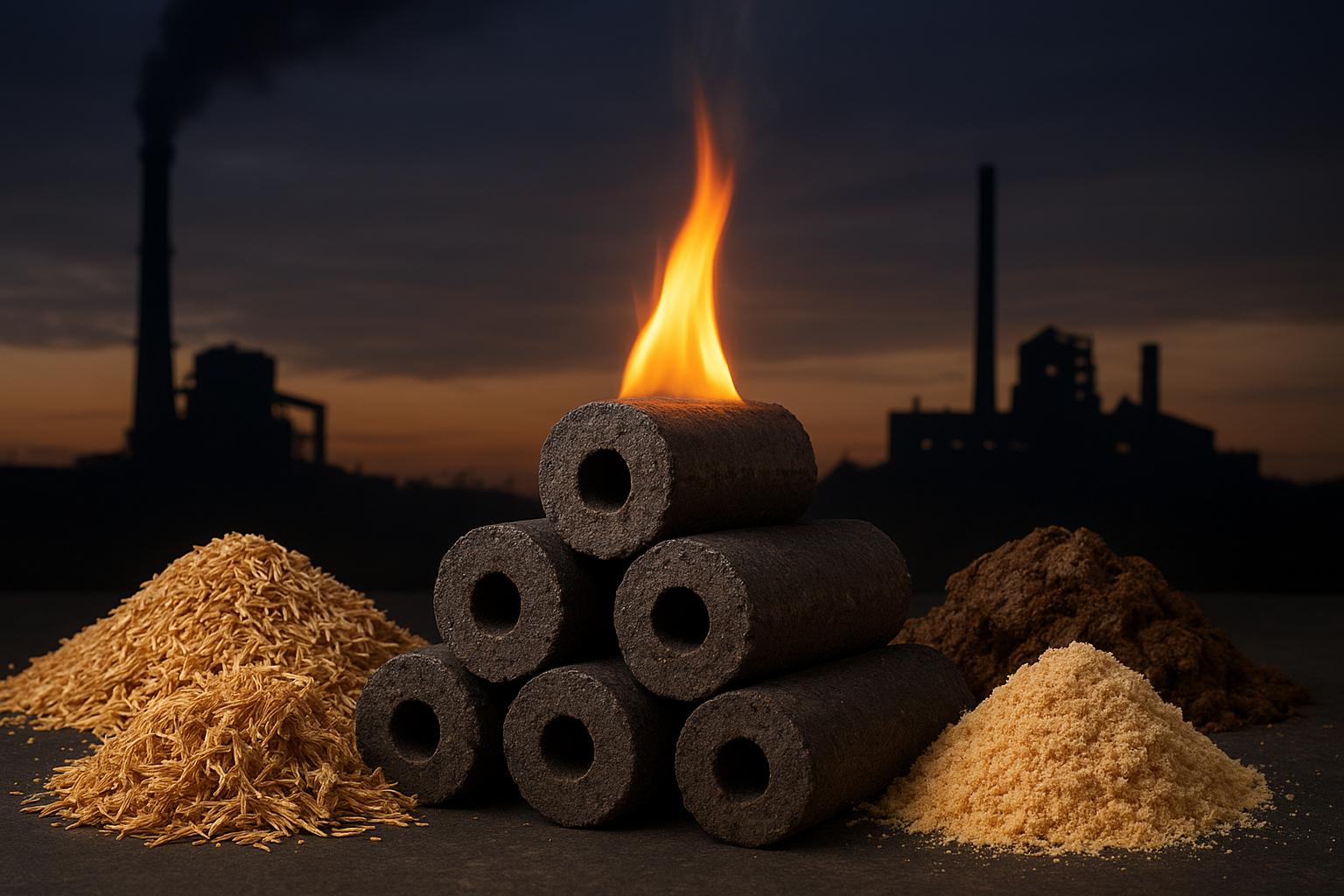
Bio-coal briquettes are the smokeless, eco-friendly fuel changing industries. Learn how they cut costs and pollution while boosting efficiency. From rice husk to cow dung, biomass briquettes are redefining clean energy. Find out why businesses globally prefer them over coal today.
If you think coal is the only fuel driving industries and households worldwide, it’s time to rethink. A quiet revolution is happening, and it’s called biomass briquettes fuel. Businesses, industries, and even households are switching, not because it’s trendy, but because it’s cost-effective, cleaner, and surprisingly powerful.
As someone who’s been tracking sustainable energy solutions, I can tell you that bio-coal briquettes are not just another green alternative—they’re a game-changer.
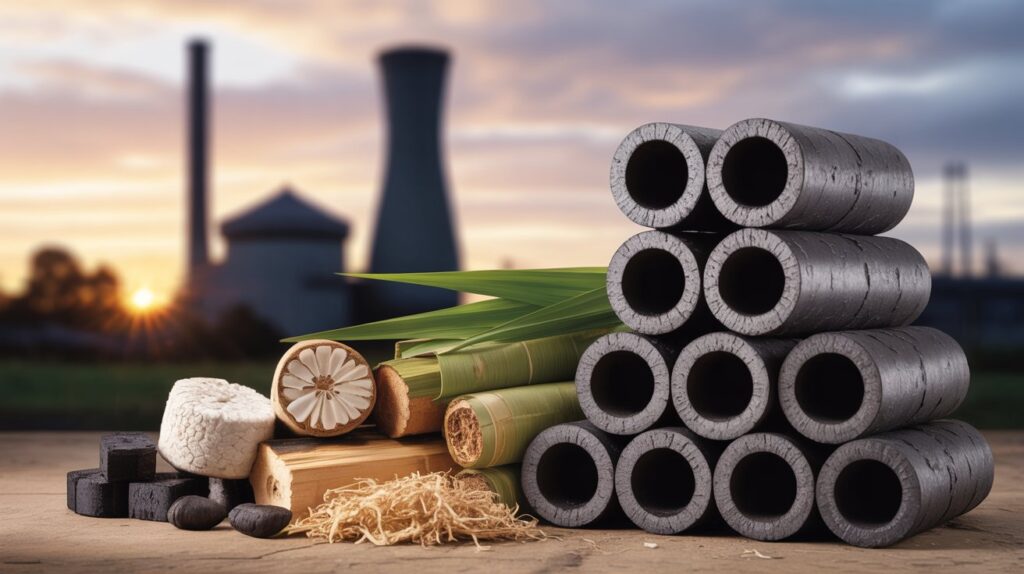

What Exactly Are Bio-Coal Briquettes?
First things first—bio-coal briquettes are not charcoal. They are an alternative biofuel created from agricultural waste and natural biomass. Imagine taking materials like rice husk, cow dung, sugarcane waste, wood husk, sawdust, groundnut shells, and dry grass—things we usually throw away—and compressing them into high-energy fuel blocks.
These briquettes are uniquely designed with a hole in the center. Why? Because this allows air to pass through, creating uniform burning. Once they catch fire, they burn with 95% smokeless efficiency—a massive improvement over traditional charcoal or coal.
Yes, there is some initial smoke when they’re lit, but as soon as they’re fully burning, the smoke almost disappears. That’s a win for cleaner air and a healthier environment.
The Science Behind the Burn
Now, here’s where it gets interesting. You might wonder: if no binding agents are used, how do these briquettes stay intact?
The answer is simple yet fascinating: lignin. This is a natural compound found in biomass. Under extreme heat (400–600 degrees Celsius) during compression, lignin oozes out. Once cooled, it acts as a natural glue, binding the entire briquette together. No chemicals, no artificial binders—just nature doing its job.
Calorific Value: How Powerful Are They?
When it comes to fuel, we always talk numbers. Bio-coal briquettes have a calorific value of 3,400–4,000 Kcal/kg, depending on the raw material used.
Compare that with charcoal, which offers about 5,000–6,000 Kcal/kg. Yes, charcoal burns hotter, but here’s the kicker: briquettes are cheaper, cleaner, and easier to handle. For industries where cost and sustainability matter more than raw burning power, bio-coal wins.
Key Features That Make Bio-Coal Briquettes Stand Out
Let’s understand more:
Ash content: Only 6%–10%. That means less residue and easier cleanup.
Moisture content: Around 6%–14%, depending on the raw material.
Burning efficiency: Once ignited, they burn steadily later with minimal smoke.
Wastage: Roughly 8%–10%, which is much lower than coal.
Cost factor: Less expensive than coal and charcoal.
Handling: Easy to store, transport, and move around without crumbling.
In simple terms, these briquettes are practical, cleaner, and cost-efficient.
How Are They Made?
The process of making bio-coal briquettes is both simple and smart. The raw materials (like cow dung, rice husk, sugarcane waste) must first be dried to a moisture content of 8%–12%. This step is crucial because excess moisture reduces burning efficiency.
Once dried, they are compressed at 400–600 degrees Celsius using specialized machines. The compression not only removes air gaps but also activates the natural lignin binder, making them strong and durable.
Two main sizes are commonly available:
50mm
70mm
These sizes are versatile enough to be used in both industrial boilers and small tandoors.
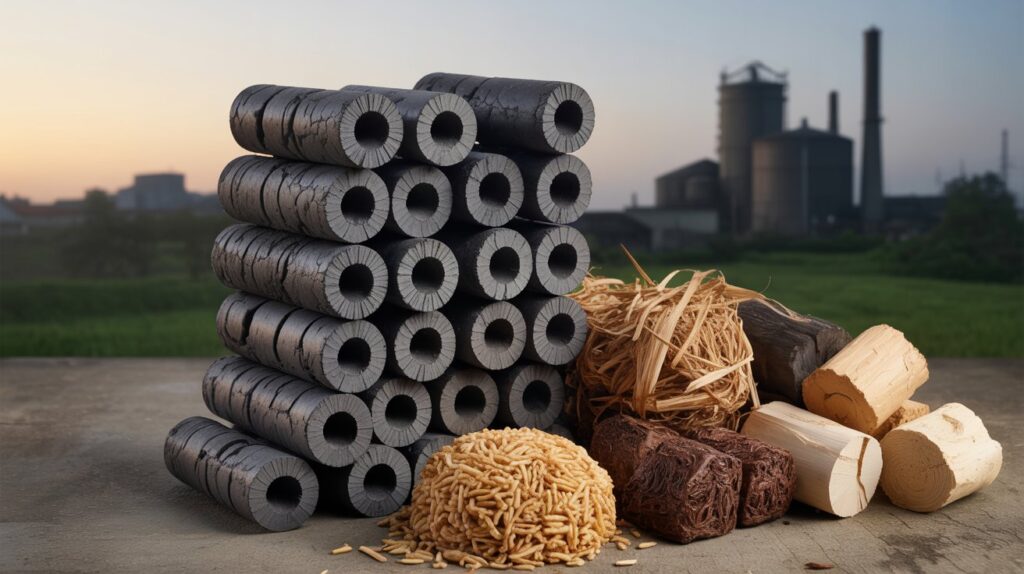

DOTE vs Non-DOTE Technology
Here’s something every industrial buyer should know. There are two types of technologies in use:
DOTE (Dry Oxidation Torrefaction Extrusion):
Produces high-quality, durable briquettes with more consistent burning. The process ensures lower moisture, better density, and higher efficiency.
Non-DOTE:
Cheaper but less efficient. Briquettes made with non-DOTE methods often have higher ash content and inconsistent burning quality.
If you’re running a large-scale operation, DOTE is worth the investment.
Production Capacity and Challenges
The production capacity depends on the raw material:
Rice husk/sugarcane waste: About 300 kg/hour.
Cow dung: Around 500 kg/hour, but it requires an extra drying process to remove excess water.
This might sound small-scale, but when scaled up with multiple machines, it can fuel entire industries.
Who Is Using Bio-Coal Briquettes?
You’d be surprised to know just how versatile these briquettes are. They’re used across large industries and small businesses alike.
Large-scale users include:
Textile mills
Brick kilns
Food industry units
Chemical plants
Dyeing houses
Leather industry
Pharma industry
Paper mills
Thermal power plants
Small-scale users include:
Restaurants
Kitchens
Home tandoors
In both cases, the biggest draw is low pollution, low cost, and clean burning.
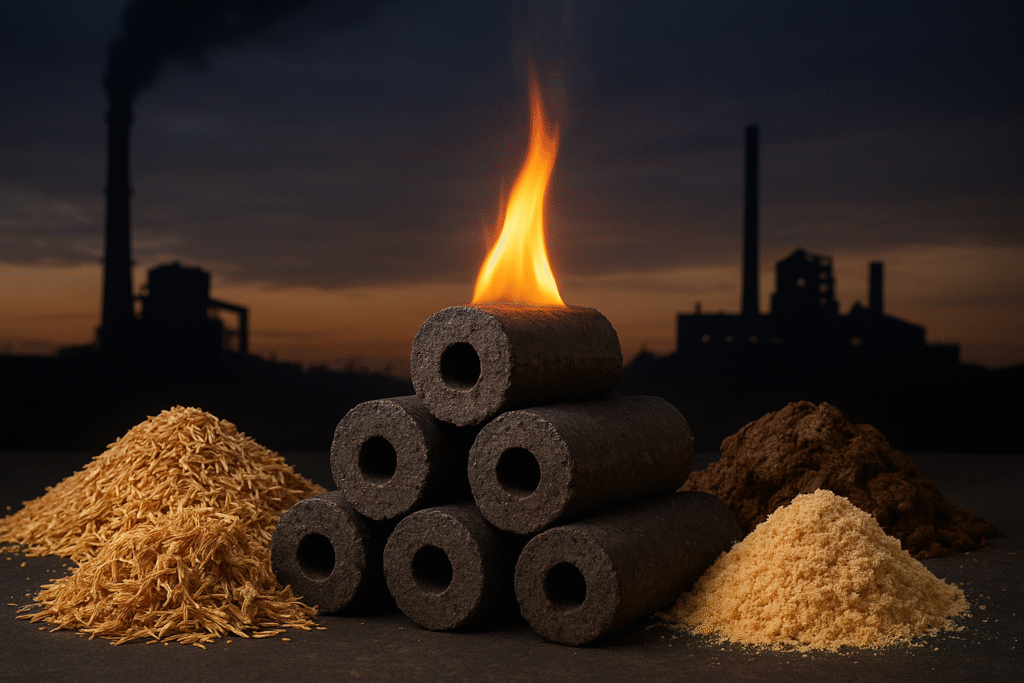

Why Industries Are Making the Switch
There are three big reasons industries worldwide are switching to biomass briquettes fuel:
1. Cost Savings: Fuel costs drop significantly compared to coal.
2. Sustainability: Companies can proudly call themselves eco-friendly by reducing carbon emissions.
3. Convenience: Easy storage and transport make them hassle-free.
For industries under increasing pressure to adopt green energy, this is the perfect middle ground—affordable and sustainable.
Final Thoughts
The world doesn’t change overnight. But right now, industries and households are looking for cleaner, cheaper, and sustainable fuels. That’s exactly why bio-coal briquettes are becoming the fuel of choice worldwide.
Yes, they don’t match charcoal in raw calorific value. But when you look at the big picture—cost savings, reduced smoke, low ash, and environmental benefits—they win hands down.
The future of fuel is not just about burning hotter, but burning smarter. And in that race, biomass briquettes fuel is clearly ahead.
If you’re a business owner, a factory operator, or even just someone curious about clean energy, keep your eye on bio-coal briquettes. They’re not just a trend—they’re the future of sustainable energy.
FAQs About Biocoal Briquettes
1. What is Biocoal Briquettes made of?
It’s made from biomass waste materials such as cow dung, rice husk, sugarcane waste, and other agricultural by-products.
2. How does it differ from regular charcoal?
Unlike traditional charcoal, it produces minimal smoke, burns longer, and is completely organic with no additives.
3. What is DOTE technology in briquettes?
DOTE (Dual Oxidification Torrefaction Extrusion Technology) enhances briquette quality, making them stronger, hotter, and more eco-friendly compared to non-DOTE alternatives.
4. Can Biocoal briquettes replace coal in industries?
Yes. Especially the 70mm briquettes, which are designed for heavy industries like steel furnaces, ceramic factories, and power plants.
5. Who should I contact to buy Biocoal briquettes?
Reach out to exporters and suppliers of biomass briquettes like Cuboid International Exports. We will provide samples for testing before bulk orders.
Conclusion
The world is moving toward cleaner energy, and biocoal briquettes are at the forefront of this transition.
If your business relies on coal — whether in hospitality, small-scale production, or heavy industries — it’s time to explore a better alternative.
Contact us at Cuboid International Exports today for a sample of Biocoal briquettes. Experience the difference in performance, cost savings, and sustainability for yourself.
Be part of the global energy revolution in 2025. Choose Biocoal Briquettes — where sustainability meets performance.